Welcome to our comprehensive US guide on how to grow your own vertical garden vegetables and maximize space in your garden. Vertical gardening is a fantastic solution for those with limited space or who want to increase their yield by utilizing the vertical dimension. In this guide, we will explore the benefits of vertical gardening, provide tips for choosing the right plants, discuss different structures for vertical gardening, offer DIY ideas, and highlight the best vegetables for vertical gardens. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, this guide will help you create a thriving vertical garden and enjoy a bountiful harvest.
Key Takeaways:
- Vertical gardening maximizes space by utilizing the vertical dimension, making it ideal for those with limited garden space.
- Benefits of vertical gardening include increased yields, easier maintenance, better disease prevention, and improved plant growth.
- Choosing the right plants for vertical gardening is crucial, with vining vegetables and fruits being ideal for training to grow upwards.
- There are various structures that can be used for vertical gardening, such as trellises, tripods, arches, pergolas, wire cages, and netting.
- DIY vertical gardening ideas include creating living walls, vegetable arches, and utilizing stackable planters to maximize space.
- Some of the best vegetables for vertical gardening include pole beans, climbing peas, vining tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash.
- Proper watering techniques, optimal sunlight exposure, and regular plant care are essential for successful vertical gardening.
- Vertical gardening can be adapted for urban areas, allowing individuals to grow their own fresh produce in limited space.
- Maintaining a vertical garden involves regular watering, pruning, and pest control to ensure healthy plant growth.
- Vertical gardening offers distinct advantages over traditional gardening methods, such as space utilization and labor efficiency.
Benefits of Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening offers numerous benefits that can enhance your gardening experience and maximize your harvest. By utilizing vertical space, you can grow more plants in a smaller area, making it ideal for those with limited garden space, such as urban dwellers. Here are some of the key benefits of vertical gardening:
- Increased Yields: Vertical gardening allows you to make the most of limited space by growing plants upwards. This maximizes the growing area available to you and can result in higher yields compared to traditional gardening methods.
- Easier Maintenance: When plants are grown vertically, they are easier to access and care for. You can say goodbye to bending and kneeling, as harvesting and tending to your plants can be done at a comfortable standing height.
- Better Disease Prevention: With plants off the ground, there is improved air circulation, which helps prevent diseases caused by waterlogged soil and excess moisture. Additionally, pests and disease symptoms are more visible, allowing for early detection and intervention.
- Optimized Sunlight Exposure: Growing plants vertically ensures that more leaf surface is exposed to sunlight, promoting healthier growth and providing optimal conditions for photosynthesis.
While there are many benefits to vertical gardening, it’s important to note that this method may require more frequent watering, especially for wall-mounted planters that may be affected by rain shadows. Consider using micro or drip irrigation systems with timers to efficiently deliver water and automate the process.
When it comes to choosing the right plants for vertical gardening, vining, rambling, and sprawling plants are ideal as they can be easily trained to grow upwards. Examples include pole beans, climbing peas, vining tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash. These plants thrive when given the support of trellises, arches, or other vertical gardening structures. Remember to provide them with the recommended 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight for optimal growth.
In addition to the benefits and plant selection for vertical gardening, it’s essential to consider the various structures available for supporting your plants. Trellises, tripods, arches, pergolas, wire cages, and netting are all viable options, and the choice depends on the characteristics and weight of the plants you intend to grow. Sturdy and well-anchored structures are necessary to provide the necessary support.
Overall, vertical gardening offers a wealth of benefits, from increased yields and easier maintenance to improved disease prevention and optimized sunlight exposure. By selecting the right plants and structures for your vertical garden, you can make the most of your available space and enjoy a bountiful harvest.
Table: Recommended Vertical Gardening Plants
| Plant | Recommended Varieties |
|---|---|
| Pole Beans | ‘Kentucky Wonder’, ‘Blue Lake’, ‘Scarlet Runner’ |
| Climbing Peas | ‘Sugar Snap’, ‘Oregon Sugar Pod’, ‘Mammoth Melting Sugar’ |
| Vining Tomatoes | ‘Sweet 100’, ‘Cherry’, ‘Roma’ |
| Cucumbers | ‘Marketmore’, ‘Burpless’, ‘Pickling’ |
| Squash | ‘Yellow Straightneck’, ‘Butternut’, ‘Acorn’ |

“Vertical gardening is a game-changer for small spaces. It allows you to grow an abundance of fresh produce without taking up precious ground space. Plus, it’s visually appealing and easy to maintain.” – Jane Doe, Gardening Enthusiast
Choosing the Right Plants for Vertical Gardening
To have a successful vertical garden, it’s crucial to choose the right plants that thrive in vertical growing conditions. Vining, climbing, and sprawling plants are ideal for vertical gardening as they can be trained to grow up and off the ground, utilizing less horizontal space. Unlike bush-type crops that take up more horizontal space on the ground, vining varieties maximize vertical space.
It’s important to consider the sunlight requirements of your chosen plants. Most vegetables generally need 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight. Therefore, select a location for your vertical garden that faces the midday sun or west to catch the afternoon sun. This will ensure that your plants receive optimal sunlight exposure, promoting healthier growth and maximizing yields. Additionally, a wall or surface that faces the sun can absorb heat during the day and reflect it back onto your plants at night, accelerating growth and harvest time.
Below is a list of recommended vegetables for vertical gardening:
- Pole beans
- Climbing peas
- Sweet potatoes
- Vining tomatoes
- Zucchini
- Cucumbers
- Melons
- Squash
Images source: seo-writing.ai
Remember to choose cultivars that are suitable for vertical growing. Some recommended varieties include:
| Vegetable | Recommended Cultivars |
|---|---|
| Cherry Tomato | ‘Sungold’, ‘Black Cherry’, ‘Gardener’s Delight’, ‘Blondkopfchen’ |
| Cucumber | ‘Burpee Hybrid II’, ‘County Fair 83’, ‘Dasher 11’, ‘Saladin’ |
| Green Bean | ‘Romano Italian’, ‘Meraviglia Venezia’, ‘Gold of Bacau’ |
| Lima Bean | ‘Doctor Martin’, ‘King of the Garden’ |
| Melon | ‘Delicious 51’, ‘Tigger’, ‘Sleeping Beauty’ (musk melon); ‘White Wonder’, ‘Yellow Doll’ (watermelon) |
| Pea | ‘Dual’, ‘Garden Sweet’, ‘Maestro’, ‘Sugar Snap’, ‘Super Sugar Snap’ |
| Squash | Acorn, delicata, yellow summer, zucchini |
When choosing vertical gardening structures, consider the characteristics of the plants you intend to grow. Tendril-producing plants like pole beans and sweet peas do well on trellises, while larger plants such as grapevines benefit from sturdier structures like arches or pergolas. Ensure that the structure can support the weight of the mature plant and is securely anchored to prevent toppling over.
Remember, vertical gardening offers space-saving benefits, easier maintenance, increased yields, and healthier plant growth. By selecting the right plants and structures suitable for vertical growing, you can maximize space utilization and enjoy a bountiful harvest.
Building Structures for Vertical Gardening
Creating a solid structure is essential for supporting your vertical garden plants and ensuring their healthy growth. There are various types of structures that can be used, depending on the specific needs of your plants and the space available.
Trellises: Trellises are one of the most common and versatile structures used in vertical gardening. They provide support for vining plants to grow upward and can be made from materials such as wood, metal, or PVC. Trellises can be placed against a wall or fence, or freestanding in the garden. They are ideal for crops like pole beans, climbing peas, and vining tomatoes.
Arches: Arches not only provide support for vertical growth but also add a decorative element to your garden. They are typically made from metal or wood and can be used to grow climbing vegetables like cucumbers and squash. The arch shape allows for easy access and harvesting of the crops.
| Structure Type | Ideal Plants |
|---|---|
| Trellises | Pole beans, climbing peas, vining tomatoes |
| Arches | Cucumbers, squash |
| Pergolas | Grapes, hops, kiwis |
| Wire cages | Tomatoes, peppers |
| Netting | Climbing plants, such as beans and peas |
Pergolas: Pergolas are larger structures that provide support for climbing plants like grapes, hops, and kiwis. They can be freestanding or attached to a wall or fence. Pergolas create a shaded area in your garden and can be used to define a walkway or seating area.
Wire cages: Wire cages are commonly used for supporting tomatoes and peppers. They provide stability and prevent the plants from sprawling on the ground. These cages can be made from sturdy wire mesh and placed around the base of the plants to provide support as they grow.
Netting: Netting is a flexible and lightweight structure that can be used to support climbing plants such as beans and peas. It is easy to install and can be draped over a frame or attached to a wall or fence. Netting provides a vertical surface for the plants to climb and helps to keep them off the ground.
When choosing a structure for your vertical garden, consider the specific needs of the plants you are growing. Ensure that the structure is sturdy enough to support the weight of the plants when they are fully grown. It’s also important to anchor the structure securely to the ground or other support to prevent it from toppling over.
By providing the right structure for your vertical garden, you can maximize the use of space, increase plant yield, and create a visually appealing garden. Experiment with different structures and find what works best for your specific gardening needs.
Quote:
“Creating a solid structure is essential for supporting your vertical garden plants and ensuring their healthy growth.”
DIY Vertical Gardening Ideas
Get creative with your vertical gardening by trying out these DIY ideas that are both functional and visually appealing.
1. Make a Living Wall
One easy way to make a vertical garden in an attractive way is a trellis panel secured onto the wall to support a range of pots planted with herbs, vegetables, and flowers. Choose an appropriate-sized panel and give it a coat of wood stain or paint to protect it and help it stand out. Drill holes into the wall with a masonry drill bit, line them with wall anchors or rawlplugs, then screw in a suitable strong L-shaped hook. Our panel below uses three. Check that the hooks are level and evenly spaced then hang up your panel. Plant up or sow your pots with low-growing crops like lettuce, pea shoots, bush beans, radishes, herbs or–for a pop of color–a few flowers like violets and marigolds. Space out the pots evenly and secure them to the trellis with sturdy garden twine, wrapped two to three times around the pot to spread its weight. Don’t forget to keep plants watered so they don’t dry out. Harvest regularly and resow, replant or reconfigure your display as needed.
2. Make a Vegetable Arch
You can make a productive walk-through vegetable arch using galvanized metal uprights and cattle panels. Clad with climbing crops like beans, cucumbers, and squash, the archway makes for easy picking – and a simply stunning way to turn utilitarian veggies into something really beautiful! Locate your vegetable archway somewhere sunny and sheltered. Start by digging out planting trenches either side of the arch. Next, drive home the uprights. Space the uprights to correspond with the width of the cattle panels. The trenches can then be backfilled, starting with a thick layer of nutrient-rich organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure, followed by the excavated soil.
Cut the cattle panels to size with wire cutters. Measure out enough of the panels to give an arch that’s high enough to walk beneath without having to stoop. Use zip ties to secure the panels to the posts at regular intervals, then trim off the excess to give a neat finish. If you’re using more than one section of cattle panel, slightly overlap the edge of the second section with the first and secure it in the same way. Plant your archway trenches with your climbing vegetables. Add a mulch of organic matter once the plants are established to lock in soil moisture and gently feed them. Most plants should find their own way up, but weave them into place if needed.
3. Stackable Planters
If space is limited, stackable planters are a great option for vertical gardening. These innovative planters allow you to grow multiple plants in a small footprint. Simply stack the planters on top of each other and fill them with soil and plants. The stackable design maximizes space and makes it easy to maintain and harvest your crops. You can grow a variety of plants in stackable planters, from herbs and vegetables to flowers and succulents. They are an excellent choice for balconies, patios, and small gardens. You can purchase stackable planters online or at garden centers, or you can even make your own using recycled materials.

Best Vegetables for Vertical Gardening
Certain vegetables are particularly well-suited for vertical gardening, offering abundant yields and easy maintenance. When choosing vegetables for your vertical garden, it’s important to consider their growth habits and how they can be trained to grow upwards. Here are some top picks for vertical gardening:
“Vining vegetables such as pole beans, climbing peas, and vining tomatoes are excellent choices for vertical gardening. They can be trained to grow up trellises, fences, or other structures, maximizing your garden space.”
These vegetables have long, flexible stems that can be easily trained to climb upwards. As they grow, you can gently guide the vines onto the trellis or support structure, helping them reach their full potential. This not only saves space but also makes harvesting easier, as the plants are at a convenient height.
In addition to vining vegetables, other options for vertical gardening include cucumbers and squash. These sprawling plants can be trained to grow vertically, allowing you to maximize space in your garden. They can be supported by trellises or cages, keeping the fruits off the ground and reducing the risk of disease or pests.
| Vegetable | Varieties |
|---|---|
| Pole Beans | Romano Italian, Meraviglia Venezia, Gold of Bacau |
| Climbing Peas | Dual, Garden Sweet, Maestro, Sugar Snap, Super Sugar Snap |
| Tomatoes | Sungold, Black Cherry, Gardener’s Delight, Blondkopfchen |
| Cucumbers | Burpee Hybrid II, County Fair 83, Dasher 11, Saladin |
| Squash | Acorn, Delicata, Yellow Summer, Zucchini |
These vegetable varieties have been proven to thrive in vertical gardening systems, providing bountiful harvests and delicious flavors. By growing these vegetables vertically, you can make the most of your available space and enjoy a productive garden.
Remember to provide proper support for your vertical garden vegetables, whether it’s a trellis, netting, or other structures. Regular maintenance, such as pruning and watering, will also be essential for their growth and success.
Maximizing Yield with Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening offers a unique opportunity to maximize yield in limited space. By growing your vegetables vertically, you can enjoy a larger harvest in a smaller footprint. This is especially beneficial for urban gardeners or those with limited garden space.
The table above provides a list of recommended varieties for vertical gardening. However, feel free to experiment with other vegetables that have vining or climbing habits. Just make sure to provide them with adequate support and train them to grow upwards.
With vertical gardening, you can create a beautiful and productive garden that not only saves space but also adds visual interest to your outdoor space. Start growing your own vertical garden vegetables and enjoy the benefits of abundant yields and easy maintenance.

Testimonial from a Vertical Gardening Enthusiast
“Vertical gardening has transformed my gardening experience. With limited space in my backyard, I was struggling to grow all the vegetables I wanted. But since I started growing vertically, I’ve been able to grow a wide variety of crops and enjoy a bountiful harvest. It’s not only practical but also visually appealing. I highly recommend vertical gardening to anyone looking to maximize their gardening space.”
– Sarah, Vertical Gardening Enthusiast
Tips for Successful Vertical Gardening
Follow these expert tips to ensure that your vertical gardening endeavor is a fruitful and enjoyable experience.
- Choose the right plants: When selecting plants for your vertical garden, opt for vining, climbing, or sprawling varieties that can be trained to grow upwards. Some suitable options include pole beans, climbing peas, vining tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash. These plants thrive in vertical gardening setups and maximize space utilization.
- Provide adequate sunlight: Most vegetables require 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight, so make sure your vertical garden is positioned in a location that receives ample sunlight. Choose a surface that faces the midday or afternoon sun for optimal sunlight exposure. It’s important to consider the sun’s position throughout the day to ensure your plants receive enough light for healthy growth.
- Water regularly: Vertical gardens, especially those mounted on walls, may need more frequent watering due to the rain shadow effect caused by the wall. Wall-mounted planters can dry out more quickly, so it’s essential to water them regularly. Consider using micro or drip irrigation systems coupled with timers to automate the delivery of water, ensuring your plants receive the right amount of hydration.
- Choose the right structure: The type of structure you choose for your vertical garden is crucial for the success of your plants. Different plants have varying growth characteristics, so it’s important to match the structure with the plant’s needs. For instance, trellises work well for leafy plants with tendrils, while more substantial plants like grapevines benefit from sturdier structures such as arches or pergolas. Ensure the structure can support the weight of the mature plants and is well-anchored to prevent toppling over.
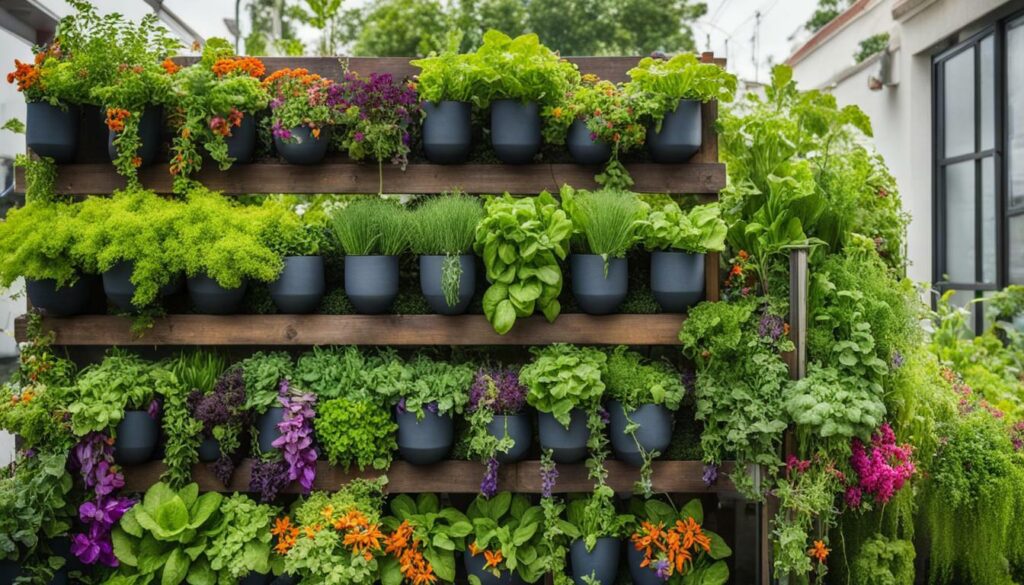

Implementing these tips will help you create a thriving vertical garden that maximizes space while providing a bountiful harvest. Remember to choose the right plants, provide adequate sunlight and water, and select the appropriate structure for your vertical garden. By following these expert tips, you’ll be on your way to a successful and rewarding vertical gardening experience.
Urban Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening is an ideal solution for urban dwellers who want to grow their own vegetables in limited space. With the increasing popularity of urban farming and the desire to maximize small yards, balconies, and rooftops, vertical gardening offers a practical and efficient way to cultivate a variety of crops. Whether you live in an apartment building or have a small backyard, you can create a thriving vertical garden that not only provides fresh produce but also adds beauty to your surroundings.
One of the benefits of urban vertical gardening is the ability to maximize the use of vertical space, making it possible to grow a wide range of plants in a small area. By utilizing trellises, tripods, arches, and pergolas, you can create a vertical garden that not only saves space but also adds structure and visual appeal to your outdoor space. Additionally, vertical gardening allows for better air circulation, which can help prevent disease and improve plant growth.
When it comes to choosing plants for your urban vertical garden, it’s important to select varieties that are well-suited for vertical growth. Vining vegetables such as pole beans, climbing peas, and vining tomatoes are excellent choices as they can be trained to grow upwards. Other vegetables that thrive in vertical gardens include cucumbers, squash, and melons, which can be trained onto trellises or supports. It’s also worth considering compact varieties of vegetables such as dwarf eggplants, lettuce, and herbs, which can be grown in hanging baskets or vertical planters.
Building structures for urban vertical gardening can be done using a variety of materials and designs. From trellises and wire cages to bamboo poles and netting, there are endless possibilities to suit your space and aesthetic preferences. It’s important to choose structures that are sturdy enough to support the weight of your plants and properly anchored to ensure stability. Consider the characteristics of the plants you plan to grow and match them with the appropriate structures for optimal growth and support.
When it comes to maintaining your urban vertical garden, it’s important to establish a regular watering schedule and provide adequate sunlight for your plants. Depending on the size and location of your vertical garden, you may need to supplement water with a drip irrigation system or use a timer to automate watering. It’s also important to monitor your plants for pests and diseases and take appropriate measures to prevent and treat any issues that may arise.
Benefits of Urban Vertical Gardening:
- Maximizes limited space
- Increases yields
- Improves air circulation and reduces disease risk
- Provides fresh and organic produce
- Adds beauty and structure to urban environments
Tips for Successful Urban Vertical Gardening:
- Choose the right plants for vertical growth
- Select suitable structures and supports
- Ensure proper watering and sunlight exposure
- Maintain regular plant care and pest control
- Harvest crops regularly for optimal growth and yield
| Vegetable | Varieties |
|---|---|
| Pole beans | ‘Blue Lake’, ‘Kentucky Wonder’, ‘Scarlet Runner’ |
| Climbing peas | ‘Sugar Snap’, ‘Snow Pea’, ‘Cascadia’ |
| Vining tomatoes | ‘Cherry Tomatoes’, ‘Roma Tomatoes’, ‘Beefsteak Tomatoes’ |
| Cucumbers | ‘Lemon Cucumber’, ‘Marketmore’, ‘Japanese Climbing’ |
| Squash | ‘Zucchini’, ‘Butternut’, ‘Delicata’ |
With the right planning, maintenance, and care, urban vertical gardening can transform even the smallest spaces into lush and productive gardens. Whether you’re a beginner or experienced gardener, vertical gardening offers a practical and efficient way to grow your own vegetables, maximize limited space, and create a green oasis in the midst of the urban jungle.
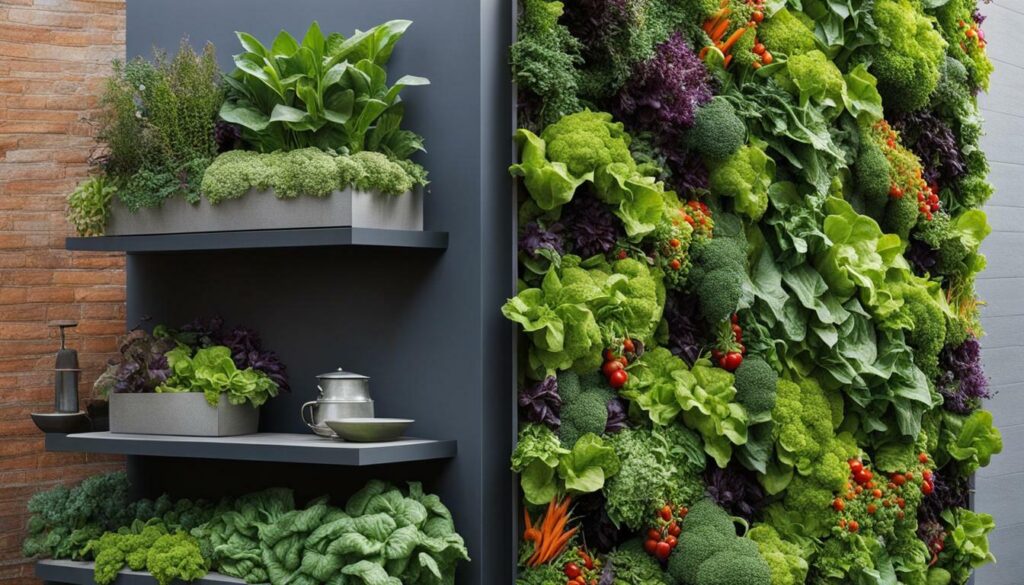

Vertical Gardening Maintenance
Keeping your vertical garden in optimal condition requires regular maintenance and attention to the unique needs of the plants. By following a few simple practices, you can ensure that your vertical garden thrives and continues to provide you with an abundance of fresh vegetables and herbs.
First and foremost, proper watering is essential for the health and productivity of your plants. Since vertical gardens typically have limited soil volume, they may require more frequent watering compared to traditional gardens. It’s important to monitor the moisture level of the soil and water as needed to prevent drought stress. Consider installing a micro or drip irrigation system that delivers water directly to the root zone of the plants, ensuring efficient and effective watering.
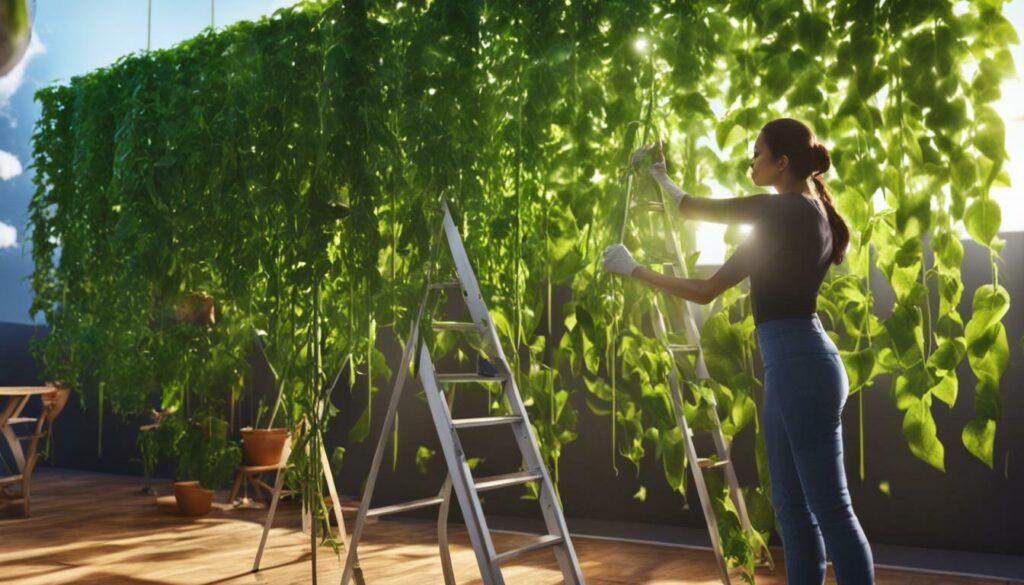

Additionally, regular pruning and maintenance of your vertical garden can help promote healthy growth and prevent overcrowding. Prune away any dead or damaged foliage and remove any weeds or unwanted plants that may compete for resources. Training vining plants to grow along trellises or supports will not only save space but also improve air circulation and reduce the risk of disease and pests.
Lastly, pest control is a crucial aspect of vertical gardening maintenance. Keep a close eye on your plants for any signs of pest infestation and take appropriate measures to control them. This can include using organic pest control methods such as handpicking pests, introducing beneficial insects, or using natural pesticides. Regularly inspect your plants for common pests like aphids, caterpillars, and spider mites, and take action promptly to prevent damage.
Table: Common Pests and Natural Pest Control Methods
| Pest | Control Methods |
|---|---|
| Aphids | – Spray plants with a mixture of water and dish soap – Introduce ladybugs, lacewings, or parasitic wasps |
| Caterpillars | – Handpick caterpillars and dispose of them – Attract birds or release beneficial nematodes |
| Spider Mites | – Spray plants with a mixture of water and neem oil – Introduce predatory mites or ladybugs |
By implementing these maintenance practices, you can ensure the long-term success of your vertical garden. Regular watering, pruning, and pest control will help keep your plants healthy and productive, allowing you to enjoy a bountiful harvest throughout the growing season.
Vertical Gardening vs. Traditional Gardening
Explore the advantages and disadvantages of vertical gardening compared to traditional gardening techniques.
Vertical gardening offers several benefits over traditional gardening methods. One of the main advantages is the ability to maximize space. By growing plants vertically, gardeners can make use of vertical surfaces such as walls, fences, and trellises, allowing them to grow more plants in a smaller area. This is particularly advantageous for those with limited garden space or urban environments where land is scarce.
Another advantage of vertical gardening is easier maintenance. With plants growing upwards, there is less bending and kneeling required for tasks such as watering, pruning, and harvesting. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with physical limitations or those who prefer a more ergonomic gardening experience.
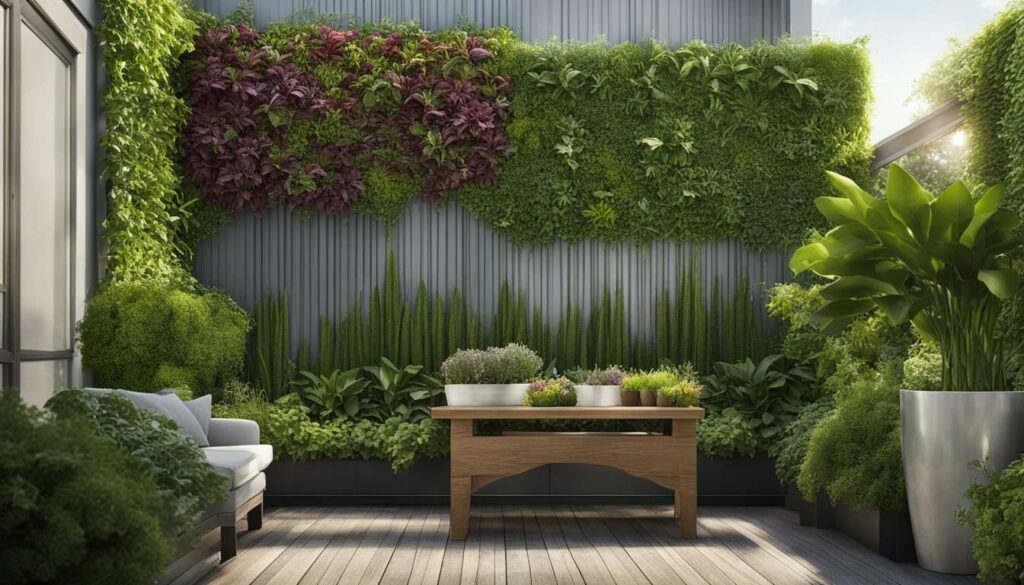

Vertical gardening also offers improved disease prevention and plant growth. By keeping plants off the ground, there is better air circulation, which reduces the risk of fungal diseases and allows plants to dry faster after watering. Additionally, vertical gardening exposes more leaf surface to sunlight, promoting healthier growth and increased photosynthesis.
However, it is important to note that vertical gardening may require more frequent watering compared to traditional gardening. Wall-mounted planters, in particular, may require regular watering due to the rain shadow created by the wall. To address this, micro or drip irrigation systems can be used to deliver water efficiently and ensure plants receive adequate moisture.
Conclusion
Vertical gardening provides an innovative and efficient way to grow your own vegetables, maximizing your garden’s potential and rewarding you with an abundant harvest. By utilizing vertical space and incorporating structures such as trellises, arches, and cages, you can expand your growing area and increase yields.
One of the key benefits of vertical gardening is the significant space-saving advantage it offers. Instead of plants sprawling on the ground, they are trained to grow upwards, reducing the need for large areas of land. This is especially beneficial for urban gardeners or those with limited space.
In addition to space savings, vertical gardening also offers several other advantages. Plants grown vertically have better air circulation, which can prevent diseases and promote healthier growth. It also makes plant care and harvesting much easier, as you can tend to your plants and pick fruits and vegetables at a comfortable height.
When choosing plants for vertical gardening, focus on vining varieties and those that can be trained to grow vertically. Popular options include pole beans, climbing peas, vining tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash. By selecting the right crops and cultivars, you can maximize your vertical garden’s productivity and optimize space usage.
Building structures for vertical gardening can be done using various materials such as trellises, tripods, arches, and wire cages. Matching the structure with the plant’s characteristics is crucial for proper support and growth. Consider factors such as the weight of the plant and the space available to determine the appropriate structure for your vertical garden.
If you’re looking for DIY ideas for vertical gardening, there are plenty of creative options to explore. From creating a living wall with trellis panels to building a walk-through vegetable arch using galvanized metal uprights and cattle panels, the possibilities are endless. Get creative and customize your vertical garden to suit your unique space and gardening preferences.
Successfully maintaining a vertical garden requires proper care and attention. Ensure your vertical garden receives adequate sunlight and water, as well as regular pruning and pest control. In urban areas, vertical gardening can be especially advantageous, making efficient use of limited space and enabling urban dwellers to enjoy the benefits of fresh homegrown produce.
When comparing vertical gardening with traditional gardening methods, it’s clear that vertical gardening offers numerous advantages. Not only does it maximize space utilization and increase the potential for a bountiful harvest, but it also reduces the strain on your back and knees, making gardening more enjoyable and accessible to a wider range of individuals.
In conclusion, vertical gardening presents a practical and efficient solution for growing your own vegetables. With the right plants, structures, and maintenance practices, you can create a thriving vertical garden that maximizes space, productivity, and enjoyment.
What Vegetables are Best for Vertical Gardening in the US?
When considering what vegetables are best for vertical gardening in the US, keep in mind the unique growing conditions. Opt for compact varieties like cherry tomatoes, lettuce, and peppers. Use trellises or stakes for support. For more vertical garden growing tips, consult a gardening expert or reliable online resources.
FAQ
Q: What are the benefits of vertical gardening?
A: Vertical gardening offers increased yields, easier maintenance, better disease prevention, and improved plant growth.
Q: Which plants are best for vertical gardening?
A: Vining vegetables such as pole beans, climbing peas, vining tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash are ideal for vertical gardening.
Q: What types of structures can be used for vertical gardening?
A: Vertical gardening structures include trellises, tripods, arches, pergolas, wire cages, netting, and more.
Q: What are some DIY ideas for vertical gardening?
A: DIY vertical gardening ideas include creating a living wall, making a vegetable arch, and using stackable planters.
Q: How do I maintain a vertical garden?
A: Proper watering, pruning, and pest control are key to maintaining a successful vertical garden.
Q: Is vertical gardening suitable for urban areas?
A: Yes, vertical gardening is a great solution for maximizing space in urban areas and can be done effectively using containers.
Q: How does vertical gardening compare to traditional gardening?
A: Vertical gardening utilizes space more efficiently and requires less labor compared to traditional gardening methods.
Q: Can vertical gardening be done on a budget?
A: Yes, vertical gardening can be done affordably by repurposing materials such as welded wire, T-posts, cattle panels, chicken wire, or recycled fencing.
Q: What are some tips for successful vertical gardening?
A: Tips for successful vertical gardening include proper watering techniques, optimal sunlight exposure, and regular maintenance.
Q: Why should I consider vertical gardening?
A: Vertical gardening allows you to maximize space, increase crop yield, and create a visually appealing and functional garden.

